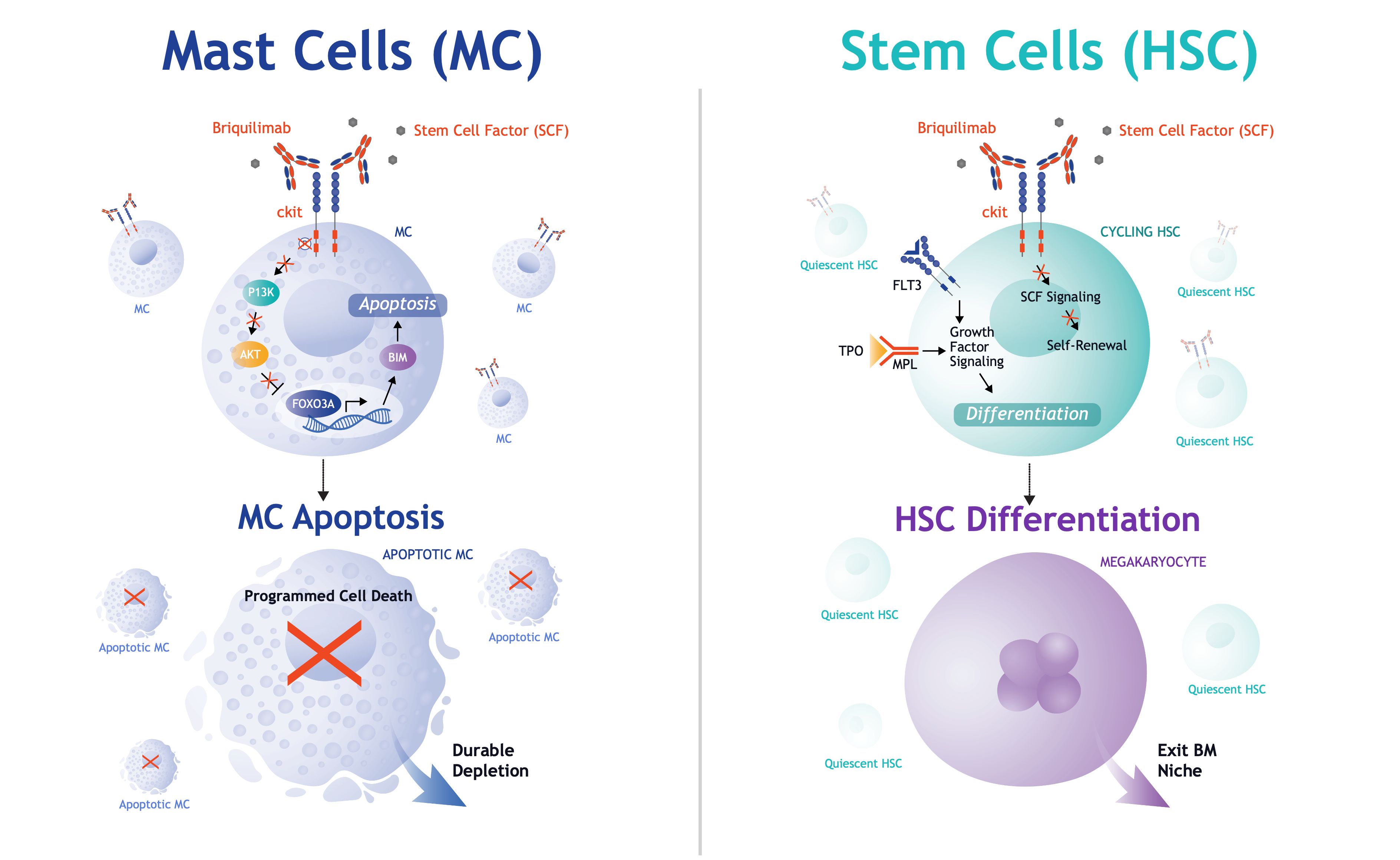
Clinical Development
To date, briquilimab has been evaluated in more than 145 healthy volunteers and patients. This humanized antibody is being studied in Jasper-sponsored clinical trials in multiple diseases.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (ongoing): Phase 1b/2a BEACON study to evaluate briquilimab as a chronic therapeutic for patients with Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria. (NCT06162728)
- Chronic Inducible Urticaria (ongoing): Phase 1b/2a SPOTLIGHT study to evaluate briquilimab as a chronic therapeutic for patients with Chronic Inducible Urticaria.
- Low to Intermediate Risk MDS (ongoing): A clinical study to evaluate briquilimab as a chronic therapeutic for transfusion dependent low to intermediate risk MDS patients. (NCT05903274)
- SCID Transplant (ongoing): Phase 1/2 dose-escalation and expansion trial is evaluating briquilimab as a sole conditioning agent to achieve donor stem cell engraftment in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for SCID, which is potentially curable only by this type of treatment. (NCT02963064)